CAUT home | Generation of the CAUT lines | Working with the CAUT lines Genetics | Seed irradiation and sector analysis | Verification of the CAUT lines
Background and theory.
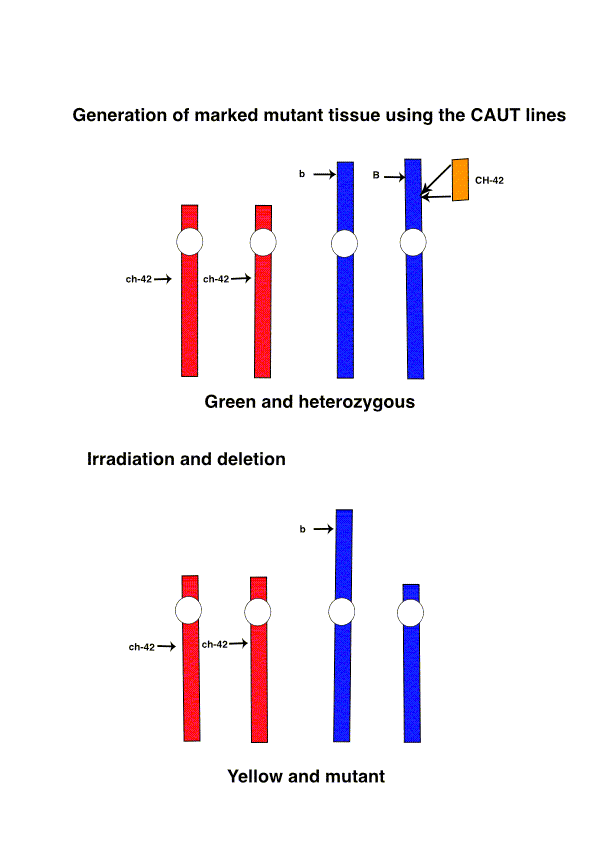
The ch-42 allele on chromosome 4 (red) is inactive but the wild-type
CH-42 function is provided by the T-DNA insert (yellow) on another
chromosome (blue). The plant is initially heterozygous for the recessive
gene b with the wild-type copy (B) linked in cis to the T-DNA. After
irradiation (lower panel) phenotypically yellow sectors are selected
and these have lost both the CH-42 copy on the T-DNA and the
adjacent B gene. The recessive b mutant is the only copy and the tissue
is both yellow and genotypically mutant. The analysis of phenotype of the
sector and adjacent wild-type tissue can be used to look for autonomous
and non-autonomous interactions.